

Chapter 3 Configuring Web Application Security
Authorization
Security constraints enable you to set various levels of authorization
within the elements of your Web application. You create J2EE roles
and map them to EAServer roles, then limit access to JSPs, servlets,
and HTML pages to entities that belong to an authorized J2EE role.
In addition, you can define which HTTP methods have access to which
URLs, and establish levels of transport guarantee.
For example, you could create a security constraint that blocks
access to all users at the Web application level. You could then
grant access to resources (HTML pages, JSPs, servlets) within the
Web application to authorized users. To do this, you need at least
two security constraints:
- Create a top-level
security constraint and assign to it a Web resource collection with
a URL pattern set to "/*".
Establish an authorized role for the security constraint that
contains no users. For example, you could create the role of "None" and
assign it to the security constraint.
- Create another security constraint and assign to
it a Web resource collection with a URL pattern set to the URL locations
for which you are providing access.
Establish an authorized role that contains the users that
are allowed access to the Web resources protected by this security
constraint.
- Create additional security constraints and allow
access to other Web resources as needed.
Use this same approach to define security constraints that
require specific levels of transport guarantee.
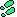 Defining a security constraint from the Web Application
Properties Security tab
Defining a security constraint from the Web Application
Properties Security tab
- Create a security constraint - click
Add to create a security constraint. Security constraints are automatically
named SC0, SC1, and so on.
To delete a security constraint, highlight the constraint
and click Delete.
- Define a Web resource collection - Web resource
collections contain a list of URL patterns and HTTP methods available
for those URLs. To define a Web resource collection:
- Highlight the security
constraint to which the Web resource collection belongs, and click
Edit.
- Click Add to create a collection name. Provide a
description.
- Highlight the collection to which you are adding
the Web resources you are protecting.
- Add a URL pattern to be protected by clicking Add
in the URL Patterns window.
- Double-click "urlPattern" and
enter the URL to be protected. Add additional URL patterns for this
collection by repeating this step.
The URL pattern can have two forms:
- /url_name - specifies
an individual URL.
- /url_location/* - specifies
all of the URLs located in the url_location directory.
- Select the HTTP operations that are allowed access
to the defined URL patterns. HTTP operations include:
- GET - the most common method
used by browsers. GET receives its input through a query string.
- POST - similar to a GET except that the
input data is sent through standard input instead of using the query
string. The POST method is normally used for an HTML form.
- PUT - same as POST except PUT usually implies
that the operation take effect immediately whereas POSTs action
may be delayed.
- OPTIONS - determines what HTTP options
are supported.
- DELETE - removes some entity.
- TRACE - causes a response with a message
containing all of the headers sent in the trace request.
-
Establish authorized roles - define
the authorized roles that have access to the HTTP methods for the
URLs defined for this security constraint. Before establishing an
authorized role, you must map EAServer roles to J2EE roles. See "Role mapping" for more information.
To configure role checking for a security constraint:
- Highlight the security
constraint to which you are adding authorized roles.
- Select Enable Authorization if role checking is
to be performed for this role. If this option is not selected, all
users have access to pages associated with this security constraint.
- Click the Authorized Roles Edit button.
- A list of mapped EAServer roles displays. Click
the check box for the roles that have permission for the Web resources
protected by this security constraint.
 To deny or allow access to all users
To deny all users access to pages associated with the security
constraint, select Enable Authorization, but do not assign any roles.To allow access to all users, deselect the Enable Authorization
option.
To deny or allow access to all users
To deny all users access to pages associated with the security
constraint, select Enable Authorization, but do not assign any roles.To allow access to all users, deselect the Enable Authorization
option.
- Transport guarantee - establish a level of
transport security for each security constraint appropriate for
the Web resources you are protecting. If you use basic or form-based
authentication, passwords and other sensitive information is not
protected for confidentiality. If you have sensitive information
that you want to protect, establish a security constraint that uses
a greater level of protection. Supported transport guarantee levels
are:
- None uses insecure HTTP. Using SSL-protected sessions has more overhead
than insecure HTTP sessions. Use None for transport guarantee if
you do not need the added confidentiality of SSL.
- Integral uses an SSL-protected session that checks for data integrity.
- Confidential uses an SSL-protected session to ensure that all message content,
including the client authenticators, are protected for confidentiality
as well as data integrity. A Confidential transport guarantee has
more overhead than None.
|
Copyright © 2002 Sybase, Inc. All rights reserved.
|

|


![]() Defining a security constraint from the Web Application
Properties Security tab
Defining a security constraint from the Web Application
Properties Security tab